AI Agent Workflows: How to Design and Orchestrate Multi-Step AI Systems
The advancement of artificial intelligence has paved the way for sophisticated AI agent workflows that can handle complex tasks by breaking them down into manageable components. As organizations increasingly rely on AI to automate processes and enhance decision-making, understanding how to design and orchestrate these workflows becomes crucial. AI agent workflows represent a fundamental shift in how we approach problem-solving with artificial intelligence, enabling multi-step processes that mimic human reasoning while leveraging machine efficiency. This article explores the intricacies of AI agent workflows, providing practical guidance on designing, chaining, and orchestrating these powerful systems.
Understanding AI Agent Workflows
Definition and Importance of AI Agent Workflows
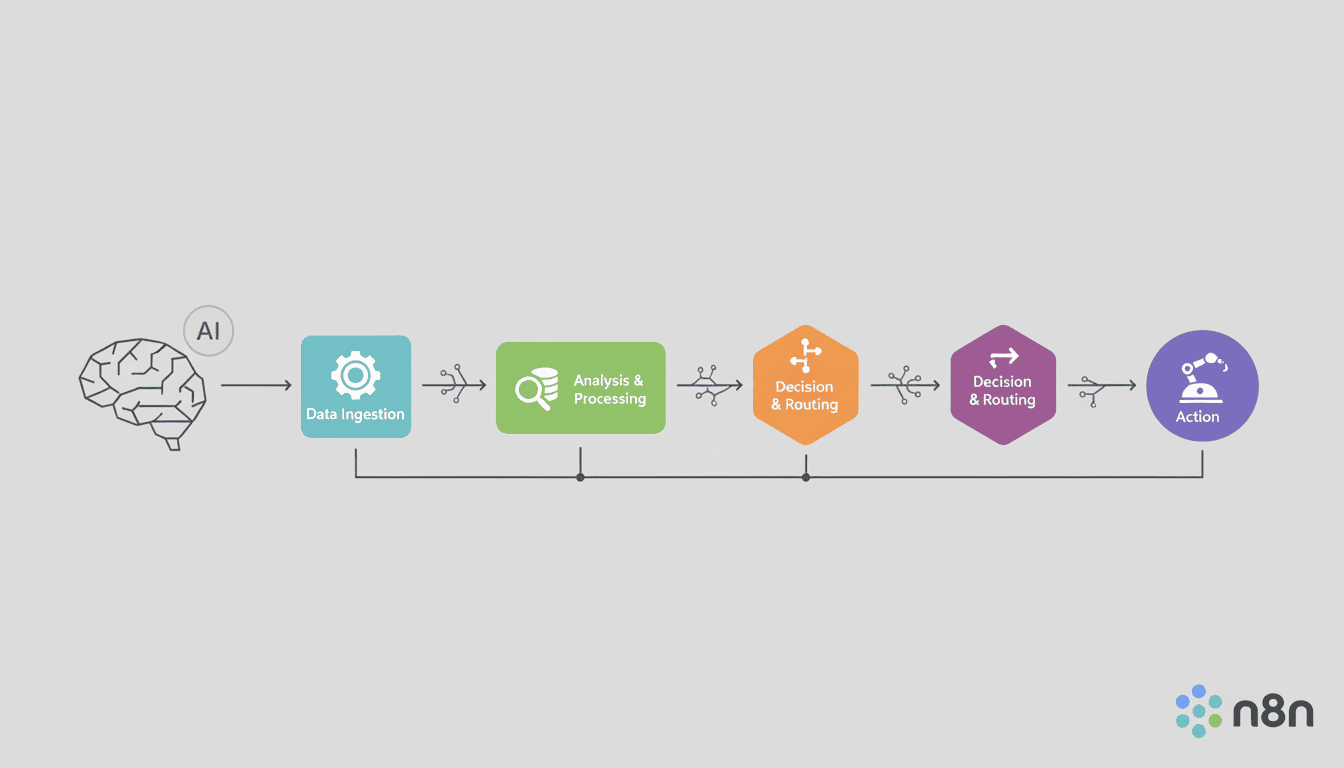
AI agent workflows are structured sequences of AI-powered operations where individual agents work together to achieve complex goals that would be difficult for a single model to handle. These workflows function like an assembly line of specialized AI workers, each contributing their expertise to solve different aspects of a problem.
The importance of AI agent workflows cannot be overstated in today’s technological landscape. They enable:
- Breaking down complex problems into manageable components
- Leveraging specialized AI capabilities for different stages of a process
- Creating scalable and reproducible solutions
- Improving overall system reliability through distributed responsibility
- Enhancing transparency and explainability of AI systems
Unlike monolithic AI applications, workflows distribute cognitive load across multiple agents, allowing each to focus on what it does best. This division of labor results in more robust solutions and clearer paths to debugging when issues arise.
Components of AI Agent Workflows
Effective AI agent workflows consist of several interconnected components:
- Individual Agents – Specialized AI models designed to perform specific tasks
- Connectors – Mechanisms for passing information between agents
- Orchestrators – Systems that coordinate agent activities and manage workflow execution
- Memory Systems – Storage for intermediate results and contextual information
- Input/Output Processors – Components that handle data formatting and transformation
Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the workflow functions smoothly. The agents themselves may range from simple rule-based systems to sophisticated language models, depending on the requirements of each step in the process.
AI Agent Workflow Design
Key Principles for Effective Workflow Design
Designing effective AI agent workflows requires adherence to several key principles:
- Single Responsibility – Each agent should have a clearly defined role and scope
- Clear Interfaces – Well-defined inputs and outputs between agents
- Error Handling – Robust mechanisms for dealing with unexpected results or failures
- Transparency – Visibility into the reasoning and operation of each workflow component
- Scalability – Ability to handle increasing workloads and complexity
The most successful AI agent workflow design approaches balance flexibility with structure. They provide enough guidance to ensure consistent results while allowing for adaptation to new situations.
Tools and Technologies for Workflow Design
Several tools and frameworks facilitate AI agent workflow design:
| Tool Category | Examples | Best Used For |
| Visual Workflow Designers | LangFlow, FlowiseAI | Rapid prototyping and visualization |
| Workflow Frameworks | LangChain, AutoGPT | Building complex agent interactions |
| Orchestration Platforms | Airflow, Prefect | Managing workflow execution and monitoring |
| Development Libraries | CrewAI, LlamaIndex | Custom agent development and integration |
These technologies simplify the process of designing, testing, and deploying AI agent workflows by providing pre-built components and standardized interfaces.
Chaining AI Agents
Methods for Chaining AI Agents
Chaining AI agents involves connecting multiple specialized agents to create a cohesive workflow. Common methods include:
- Sequential Chaining – Agents execute in a predetermined order, with each agent’s output serving as the next agent’s input
- Parallel Chaining – Multiple agents work simultaneously on different aspects of a problem
- Recursive Chaining – Agents can call themselves or other agents recursively to solve sub-problems
- Dynamic Chaining – The sequence of agent execution is determined at runtime based on intermediate results
Each chaining method offers distinct advantages depending on the nature of the problem being solved. Sequential chaining provides simplicity and predictability, while dynamic chaining offers greater flexibility for complex scenarios.
Best Practices for Successful Chaining
To ensure successful AI agent chaining:
- Standardize data formats between agents to minimize transformation overhead
- Implement robust error handling at each transition point
- Monitor performance bottlenecks in the chain
- Design for graceful degradation if an agent fails
- Include validation checks between agent handoffs
Creating Multi-Step AI Workflows
Designing Multi-Step Workflows: A Step-by-Step Guide
Designing effective multi-step AI workflows involves:
- Problem Analysis – Clearly define the overall objective and break it down into discrete steps
- Agent Selection – Identify which specialized agents are needed for each step
- Workflow Architecture – Determine how agents will be connected and how information will flow
- Interface Design – Define the input/output specifications for each agent
- Error Handling Strategy – Plan for potential failures at each step
- Testing Framework – Create comprehensive tests for individual agents and the entire workflow
- Monitoring Plan – Establish metrics to track workflow performance
This methodical approach ensures that multi-step AI workflows are both robust and maintainable.
Common Challenges in Multi-Step Workflows and How to Address Them
Multi-step AI workflows often face several challenges:
- Error Propagation – Small errors in early steps can amplify through the workflow
- Context Loss – Important information may be dropped between agents
- Performance Bottlenecks – Slow agents can delay the entire workflow
- Complexity Management – As workflows grow, they become harder to maintain
Address these challenges by implementing comprehensive testing, creating fallback mechanisms, optimizing critical paths, and documenting workflow logic thoroughly.
AI Agent Orchestration
Understanding AI Agent Orchestration
AI agent orchestration involves coordinating the execution of multiple agents in a workflow, managing resources, handling failures, and ensuring optimal performance. Unlike simple chaining, orchestration adds a layer of intelligence that can make decisions about workflow execution in real-time.
Effective orchestration systems provide:
- Dynamic scheduling of agent execution
- Resource allocation based on priority and availability
- Monitoring and logging of workflow execution
- Failure recovery mechanisms
- Performance optimization through caching and parallel processing
Tools for AI Agent Orchestration
Several tools facilitate AI agent orchestration:
- Apache Airflow – Open-source platform for workflow orchestration with strong scheduling capabilities
- Prefect – Modern workflow orchestration with failure recovery and observability
- Temporal – Durable execution system for reliable workflow orchestration
- Langsmith – Specialized for LLM workflow orchestration with debugging capabilities
- Kubernetes – Container orchestration that can be adapted for AI workflow management
AI Workflow Examples
Case Studies of Successful AI Workflows
Several organizations have successfully implemented AI agent workflows:
- Customer Support Automation – A financial services company implemented a multi-agent workflow that triages customer inquiries, retrieves relevant account information, generates appropriate responses, and escalates complex issues to human agents when necessary.
- Content Generation Pipeline – A media organization uses a workflow that combines research agents, content structuring agents, writing agents, and editing agents to produce high-quality articles at scale.
- Medical Diagnosis Assistant – A healthcare provider deployed a workflow where different agents handle symptom analysis, medical history review, potential diagnosis suggestion, and treatment recommendation review.
These examples demonstrate how well-designed AI agent workflows can tackle complex problems by breaking them into manageable components.
Innovative Use Cases for AI Agent Workflows
Emerging applications of AI agent workflows include:
- Autonomous Research – Workflows that can search, synthesize, and analyze information across multiple sources
- Creative Collaboration – Systems where specialized agents contribute different aspects to creative works
- Personalized Education – Adaptive learning systems that tailor content and feedback based on student performance
- Complex Decision Support – Workflows that evaluate options across multiple dimensions and provide structured recommendations
These innovative applications highlight the versatility of AI agent workflows in addressing challenges across diverse domains.
Resources
Recommended Tools and Platforms
To get started with AI agent workflows, consider these resources:
- LangChain – Framework for developing applications powered by language models
- CrewAI – Framework for orchestrating role-playing autonomous AI agents
- AutoGPT – Experimental open-source application showcasing GPT-4’s capability to chain together LLM calls
- LlamaIndex – Data framework for LLM applications to connect custom data sources
- Microsoft Semantic Kernel – SDK that integrates AI services into applications
Further Reading and Learning Opportunities
Deepen your understanding of AI agent workflows through these resources:
- “Building LLM Powered Applications” by Simon Willison
- “Designing Multi-Agent Systems: A Practical Guide” by Munindar P. Singh
- Stanford’s “CS224N: Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning”
- LangChain documentation and tutorials
- Hugging Face’s course on building with LLMs
Conclusion
AI agent workflows represent a powerful approach to solving complex problems by breaking them down into manageable steps handled by specialized AI components. By following sound design principles, implementing effective chaining strategies, and leveraging robust orchestration tools, organizations can create sophisticated AI systems that outperform monolithic approaches.
As the field continues to evolve, we can expect AI agent workflows to become increasingly important in developing reliable, explainable, and powerful AI applications. The flexibility and modularity of workflow-based approaches make them well-suited for addressing the diverse challenges organizations face today.
By mastering the design and orchestration of AI agent workflows, developers and organizations can unlock new capabilities, improve efficiency, and create more sophisticated AI-powered solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between AI agent workflows and traditional automation?
AI agent workflows differ from traditional automation by incorporating intelligent, adaptive components that can handle unstructured data, make decisions under uncertainty, and learn from experience. Traditional automation typically follows rigid, predetermined rules without the flexibility to adapt to novel situations or unstructured inputs.
How do I determine if my problem is suitable for an AI agent workflow approach?
Problems well-suited for AI agent workflows typically require multiple types of reasoning or expertise, involve complex decision-making that can be broken into discrete steps, and benefit from specialized handling at different stages. If your problem can be clearly decomposed into subtasks that could each benefit from different AI capabilities, it’s likely a good candidate.
What skills are needed to design effective AI agent workflows?
Designing effective AI agent workflows requires a combination of systems thinking, AI/ML knowledge, software architecture principles, and domain expertise. Understanding prompt engineering, LLM capabilities and limitations, data flow management, and error handling are particularly important skills.
How can I measure the performance of an AI agent workflow?
Performance measurement should include both process metrics (execution time, resource usage, error rates) and outcome metrics (accuracy, quality of results, user satisfaction). Additionally, tracking performance at each step in the workflow helps identify bottlenecks and improvement opportunities.
What are the costs associated with implementing AI agent workflows?
Costs include development time, infrastructure for running the workflow, API usage fees for commercial AI models, ongoing maintenance, and monitoring. However, well-designed workflows can reduce costs by using specialized, efficient models for each step rather than relying solely on more expensive general-purpose models for all tasks.
How do I ensure my AI agent workflow is reliable and secure?
Reliability comes from comprehensive testing, graceful error handling, monitoring, and fallback mechanisms. Security requires careful attention to data handling, authentication between components, input validation, and output sanitization. Regular auditing and implementing least-privilege principles for each agent in the workflow are also crucial practices.